Gynecology and Obstetrics
Gynecological Operations
There are many reasons why a woman might need to undergo gynecology surgery. She may need treatment for a condition such as endometriosis, fibroids (benign tumors), ovarian cysts, cancer, chronic pelvic pain, pelvic inflammatory disease, uterine prolapse or abnormal bleeding.
The common tepesi of gynecological operations below:
- Hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is a procedure to remove the uterus. - Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy (TLH)
TLH is the removal of the uterus and cervix through four small abdominal incisions. - Laparoscopic Supracervical Hysterectomy (LSH)
This procedure involves laparoscopic removal of the uterus and the patient is able to keep her cervix. - LEEP Procedure
When a PAP smear indicates abnormal cells on the surface of the cervix, a healthcare provider may recommend a loop electrosurgical excision procedure. - Pelvic Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure usually performed under general anesthesia.
Robotic-Assisted Surgery
In robotic-assisted surgery, the surgeon uses a computer-controlled device that moves, positions, and manipulates surgical tools based on his or her movements.
Removing Uterine Polyps
Uterine polyps are noncancerous cells that grow on the inner wall of the uterus and extend to the uterine cavity
Laparoscopic Assisted Vaginal Hysterectomy (LAVH)
LAVH is a surgical procedure using a laparoscope to guide the removal of the uterus and/or fallopian tubes and ovaries through the vagina.
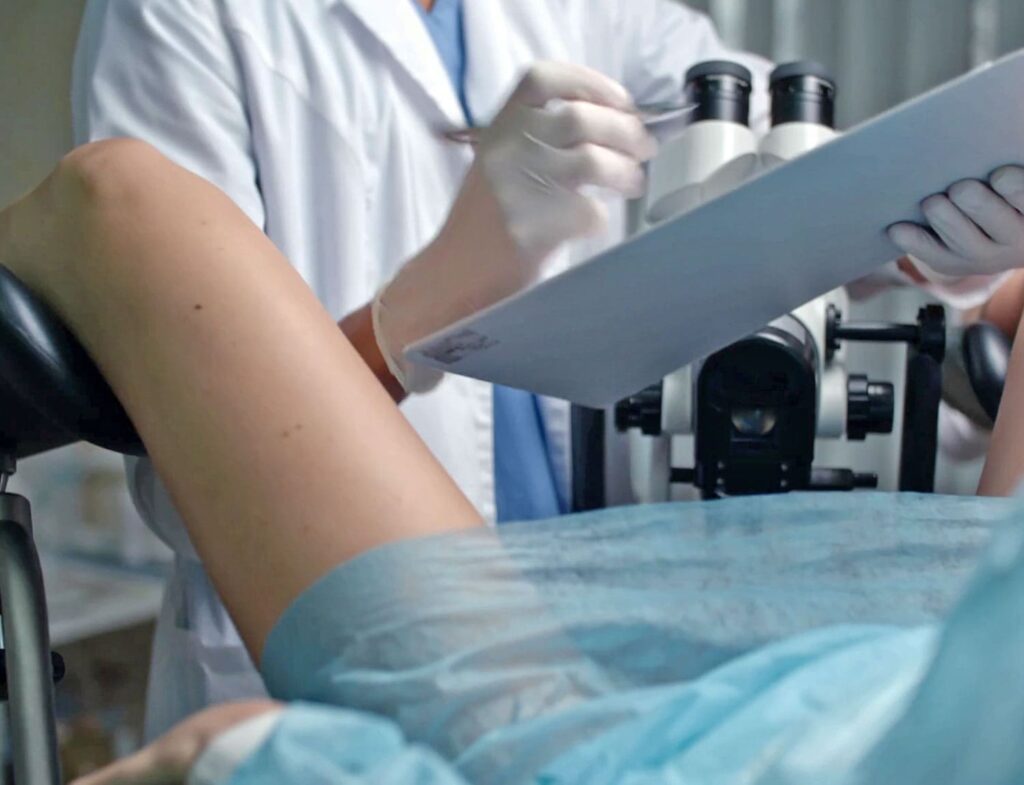
Colposcopy
A colposcopy is a non-surgical diagnostic tool used to examine the cervix, vagina, and vulva more closely. It is sometimes used when a person has an abnormal Pap smear.3
During the procedure, a healthcare provider uses a colposcope, a magnifying instrument. If an area appears concerning during this procedure, they may take a sample and send it to the laboratory for testing.



